Major Projects
Staff Undertaking Skills To Advance Innovation (SUSTAIN)
 Staff Undertaking Skills To Advance Innovation (SUSTAIN) is a supervision model that fosters knowledge and skill building via a web-based curriculum plus in-person coaching. The web-based curriculum consisting of nine core training modules designed to facilitate knowledge gain and use of practices that reduce criminal behavior. Evidence-based practices (EBPs) included in the SUSTAIN curriculum are based on policies and procedures that have demonstrated solid empirical support for their use. Examples of EBPs include engagement techniques, case management practices, and teaching individual’s problem -solving skills, all of which promote desistance from crime. The eLearning curriculum also introduces a set of interactional and cognitive skills to help promote the understanding and use of Core Correctional Practices. All users are introduced to the practices, and jurisdictions have the option of getting in-depth coaching.
Staff Undertaking Skills To Advance Innovation (SUSTAIN) is a supervision model that fosters knowledge and skill building via a web-based curriculum plus in-person coaching. The web-based curriculum consisting of nine core training modules designed to facilitate knowledge gain and use of practices that reduce criminal behavior. Evidence-based practices (EBPs) included in the SUSTAIN curriculum are based on policies and procedures that have demonstrated solid empirical support for their use. Examples of EBPs include engagement techniques, case management practices, and teaching individual’s problem -solving skills, all of which promote desistance from crime. The eLearning curriculum also introduces a set of interactional and cognitive skills to help promote the understanding and use of Core Correctional Practices. All users are introduced to the practices, and jurisdictions have the option of getting in-depth coaching.
SUSTAIN was originally developed under a grant funded by the Bureau of Justice Assistance (2010-DB-BX-K077) with Ralph Serin of University of Ottawa. The original material was developed by both laboratories.
Key Staff:
- PI: Faye S. Taxman, Ph.D.
- Co-developers: Heather Toronjo, MPP; Stephanie Ainsworth Maass, Ph.D. (Norwich University)
- Project Manager: Amy Murphy
Funding Source: BJA: 2010-DG-BX-K026
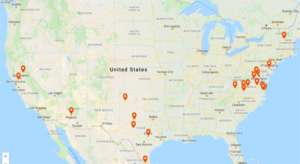 Study Locations: Hidalgo (TX) County Community, Solano (TX) County Community, Travis (TX) County Community, Nevada (CA) County Community, Potter County Community, Tom Green/Concho Valley, Phoenix, Arizona, Philadelphia, PA and the Commonwealth of Virginia.
Study Locations: Hidalgo (TX) County Community, Solano (TX) County Community, Travis (TX) County Community, Nevada (CA) County Community, Potter County Community, Tom Green/Concho Valley, Phoenix, Arizona, Philadelphia, PA and the Commonwealth of Virginia.
Major Goal:
SUSTAIN is meant to foster the ongoing professional development of staff in community corrections agencies. Specifically, staff development centered around both “what works” and also the values laid out by Executive Session on Community Corrections.
The SUSTAIN model aims to create a learning environment when all staff are encouraged to practice skills and ask questions. To achieve these larger aims of staff professionalization, SUSTAIN lays out the following four overarching goals and the specific objectives associated with each:
- Improve staff perception of the acceptability, appropriateness, and feasibility of evidence-based supervision methods.
- Transform the role of supervisors/middle managers from boss to coach. Goal 3. Improve supervisors’ coaching skills.
- Improve front-line officers’ use of core correctional practices.
Major Implementation Lessons:
Acceptability – Staff must believe EBPs are credible. That they work. Coaches must believe that coaching staff works to improve professional practice.
Appropriateness – Staff must believe EBPs are appropriate. In other words, that EBPs are the right thing to do in their agency. Coaches must believe that coaching is appropriate part of their job as a supervisor.
Feasibility – Feasibility issues include time and integration of practices. Coaches need time to conduct observation and coaching, and officers need help with integrating practices into everyday supervision processes.
Fidelity – Coaches should use the coaching skills learned in training with staff and staff must use evidence-based practices true their original intention and character.
Sustainability – Agencies should plan how new coaches be trained, how new officers will be trained, and who will be responsible for collecting and reviewing observation data.
Successful implementation requires the following:
- Enthusiastic leadership
- Review of policies and procedures to assess alignment or disagreement with evidence- based supervision practice
- Have a coaching service delivery plan that details the why, what, when, and how of coachi
- Set expectations by 1) explaining why SUSTAIN is important for agency mission, 2) detailing exactly what staff can expect over the two-year rollout, and 3) answering all staff questions.
Publications
Toronjo, H. (2019). Gut Check: Turning experience into knowledge in P. Ugwudike, H. Graham, F. McNeill, P. Raynor, P., F. Taxman, & C. Trotter, C. (Eds.), in Routledge companion to rehabilitative work in criminal justice. London, England: Routledge.
Toronjo, H. (2019). A corrections workforce for the 21st century. Federal Probation. 83(1), 3-7.
Toronjo, H. & Taxman, F. (2018). Supervision face-to-face contacts: the emergence of an intervention in Ugwudike, P. Raynor, P. and Annison, J. (eds) Evidence-Based Skills in Criminal Justice: International Research on Supporting Rehabilitation and Desistance. Bristol & Chicago: Policy Press.
Murphy, A., Maass, S.A., and Taxman, F.S. (2017). Using Translational Tools to Reduce Recidivism in Hidalgo County, Texas. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, Bureau of Justice Assistance.
Toronjo, H., & Maass, S., Murphy, A., Taxman, F. (2015) Smart Probation in Philly: Skills for Offender Assessment and Responsivity in New Goals (SOARING2) Organizational Survey Results.
Select Presentations
Ainsworth, S.A. (2012, November). Effectiveness of an eLearning Program for Probation Officers. Presented at the American Society of Criminology Annual Conference, Chicago, IL.
Maass, S.A. (2013, May). Increasing Use of Evidence-Based Practices Through an eLearning Training Program: SOARING 2. Presented at the Law & Society Association Annual Conference, Boston, MA.
Maass, S. A. (2016, August). What works in improving training outcomes? Keynote address given at the Virginia Department of Corrections Research in Motion Conference, Richmond, VA.
Maass, S.A. (2016, November). Individual, Organizational, and Training Design Influences on Probation Training Outcomes. Poster presented at the American Society of Criminology Annual Conference, New Orleans, LA.
Maass, S.A., Crites, E., & Taxman, F.S. (2013, July). Implementing Evidence-Based Practices in Community Corrections. Presented at the American Probation and Parole Association Conference, Baltimore, MD.
Maass, S.A., Duhaime, L., & Serin, R. (2013, September). SOARING 2 Pilot Summary. Presented at the International Association of Community Corrections Association, Reno, NV.
Maass, S. A., Taxman, F.S., Serin, R., Crites, E., Watson, C.A., & Lloyd, C. (2013, November). SOARING 2: An eLearning Training Program to Improve Knowledge of EBPs. Presented at the American Society of Crime in Annual Conference, Atlanta, GA.
Taxman, F.S., Maass, S.A., Perez, R., Lopez, F., & Torres, J. (2014, October). Coaching to Improve Fidelity in Community Corrections. Presented at the 42nd Annual Chief Probation Officers Conference, Galveston, TX.
Taxman, F.S., Serin, R., Maass, S.A., Crites, E., Watson, C.A., & Lloyd, C. (2013, March). SOARING 2: A Web-Based Training Program for Community Corrections Officers. Poster presented at the DC Health Communication Conference, Fairfax, VA.
Toronjo, H. (2017, November ).Understanding the Coaching Gap: Lessons from Psychology and Social Work .Presented at the American Society of Criminology Conference, Philadelphia, PA.
